CS Study/알고리즘
정렬 알고리즘 (버블, 선택, 삽입) + 자바구현
danalee252
2022. 3. 25. 23:13
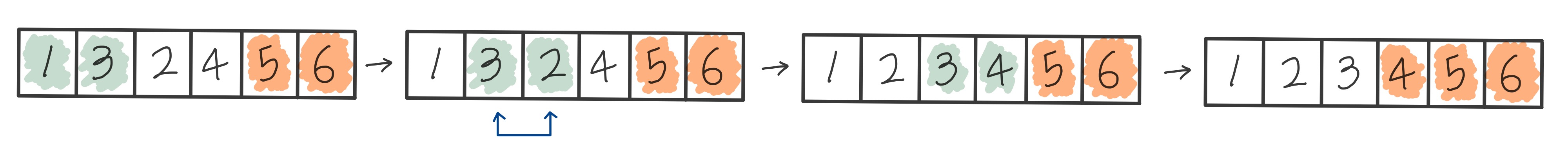
버블 정렬 (Bubble Sort)
- 인접한 두 요소를 비교하여 왼쪽 요소가 오른쪽 요소보다 크면 서로 바꾼다.
- 배열의 끝까지 비교하면 마지막 요소는 그 위치가 최종적으로 정렬된 요소이다.
- 다시 처음으로 돌아와서 두 요소끼리 비교하며 자리를 바꾼다.
- 배열의 크기가 N이라면, (N-1) + (N-2) + ... + 1 = N * (N-1) / 2번 비교를 수행한다.
- 시간복잡도: O(N^2)




자바 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scn.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = scn.nextInt();
}
for (int i = n-1; i > 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]) {
int tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = tmp;
}
}
}
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
선택 정렬 (Selection Sort)
- 첫 번째 요소부터 시작하여 가장 작은 요소를 찾아 현재 요소와 자리를 바꾼다.
- 시간복잡도: O(N^2)

자바 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SelectionSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scn.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = scn.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int min = i-1;
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[min] > arr[j]) {
min = j;
}
}
int tmp = arr[i-1];
arr[i-1] = arr[min];
arr[min] = tmp;
}
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
삽입 정렬 (Insertion Sort)
- 배열의 두 번째 요소부터 시작한다.
- 현재 요소의 왼쪽 구역(정렬이 완료된 구역)을 보면서 현재 요소의 위치를 찾아 삽입한다.
- 시간복잡도: 최적의 경우 O(N), 최악의 경우 O(N^2)

자바 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class InsertionSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scn.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = scn.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int current = i;
for (int j = 1; j < i+1; j++) {
if (arr[current] < arr[i-j]) {
int tmp = arr[current];
arr[current] = arr[i-j];
arr[i-j] = tmp;
current = i-j;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}